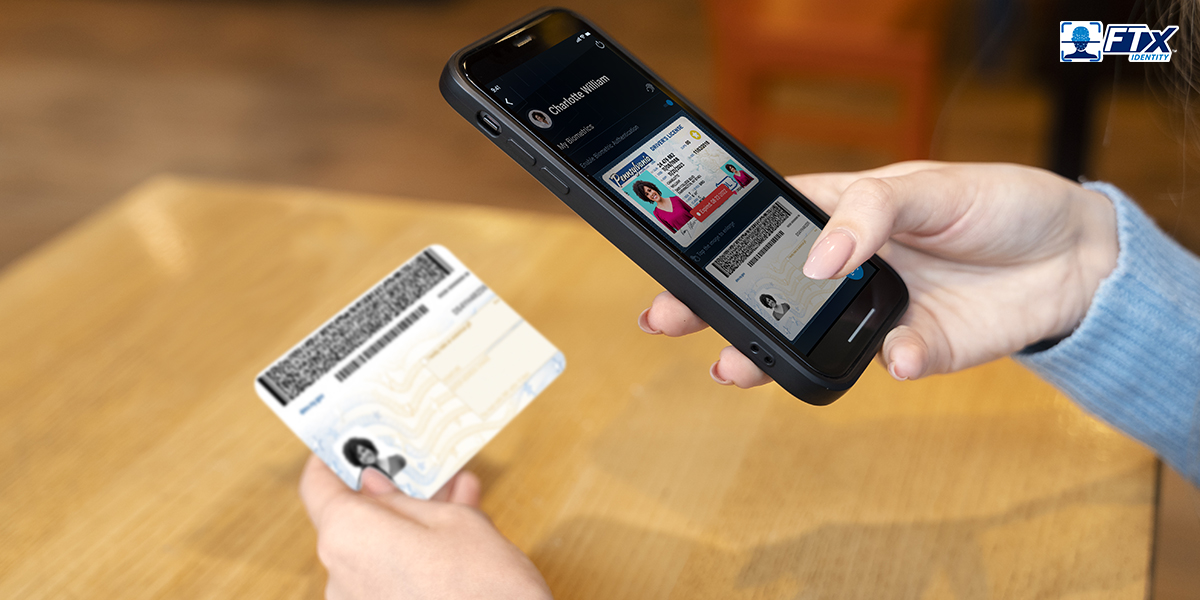
Identity verification is crucial in today’s increasingly online world. ID verification technology prevents fraud and identity theft, protects private information, and saves businesses money. Plus, it builds trust with customers.
In fact, the identity verification market is expected to reach $21.07 billion by 2028.
Businesses can take advantage of the convenience of automation and real-time verification. Customers can also experience a quick and user-friendly verification process while being reassured that their personal information is safe.
But if you want to use it in your business, it’s important that you know exactly what AI identity verification is, how it works, and key benefits.
In this piece, we’ll fill you in on everything you need to know.
Understanding AI Identity Verification
What Is AI ID Verification?
AI ID verification refers to the use of artificial intelligence technologies to confirm the identity of an individual. Traditional methods of identity verification included providing physical documents, answering security questions, and inputting access codes.
However, when we discuss the traditional vs. AI-Based Identity Verification Methods, we all know the AI-powered identity verification takes it to a whole new level.
In place of these old-school methods, our faces, driver’s licenses, and passports are scanned. Even our typing patterns and mouse movements are analyzed, thanks to the power of AI.
Types of Identity Verification
There are different ways to make sure someone is who they say they are. The best way depends on how secure you need it to be and what the user experience should be like.
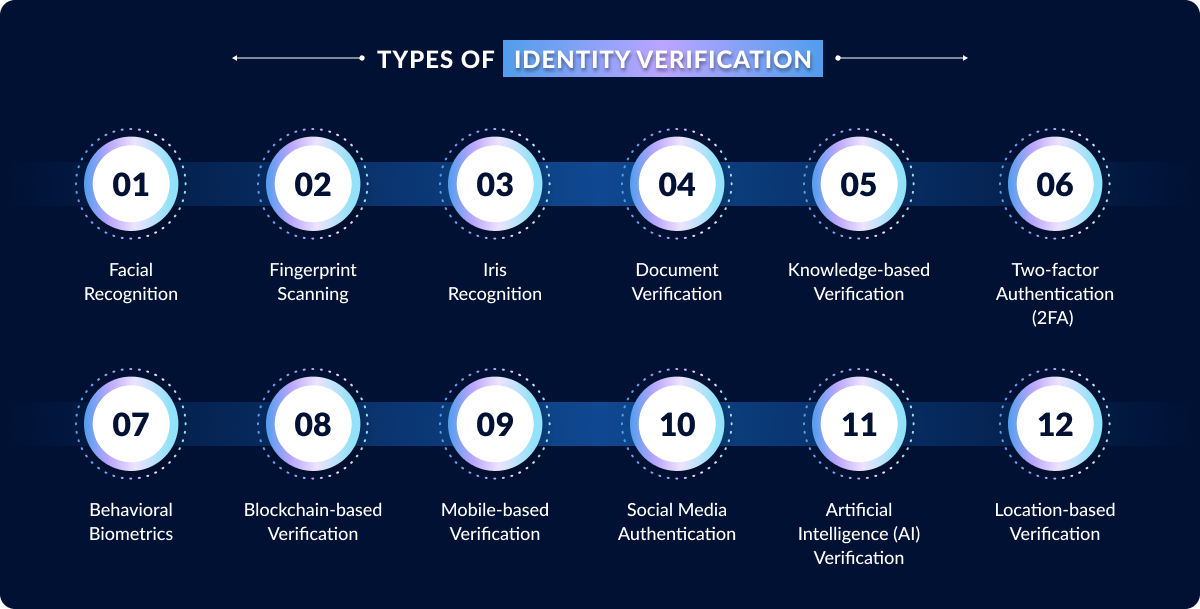
1. Facial Recognition
It is a contactless and convenient method that uses sophisticated algorithms to analyze and compare human faces for user identification. This typically includes comparing facial features from a photo captured by a camera to data within a database of known faces to identify a match.
Curious about how to protect your business and customers? Safeguard your brand, comply with regulations, and create a secure environment for your customers. Check out how it works for your business.
2. Fingerprint Scanning
In this process, fingerprints are used to provide users access to information or authorize transactions. It operates by using the unique patterns of ridges and valleys on a person’s fingers to confirm their identity.
3. Iris Recognition
It uses unique patterns of the colored part of a user’s eye (the iris) to verify their identity. Once a picture of the eye is taken, complex algorithms examine the unique features of the iris. Finally, the iris features extracted are compared to a stored database of iris patterns. If there’s a match, the user’s identity gets confirmed.
4. Document Verification
Document verification using AI involves confirming if government-issued documents like driver’s licenses, passports, or ID cards are valid. This process involves visually inspecting the document for any tampering signs, like ink smudging or discrepancies in holograms or watermarks.
Some examples of common uses include opening a bank account, checking employment records, and verifying users during online transactions.
5. Knowledge-based Verification
Knowledge-based Verification consists of verifying a user’s identity by asking them questions regarding information that only they should know. Examples include asking security questions during onboarding like “What is your paternal grandmother’s name?” or “Where did you go to high school?”.
Typically, these questions are created based on the user’s unique profile and are designed to be challenging to answer for someone who doesn’t have access to the information.
6. Two-factor Authentication (2FA)
It’s described as an extra layer of security that’s designed to confirm a user is who they say they are by requiring two forms of identification to authenticate them. Doing so makes it challenging for hackers to get access to a user’s information. A common form of 2FA is sending a code via email or text when a user forgets their password to log into a portal.
7. Behavioral Biometrics
This approach examines how users physically engage with a website or mobile app. This measures everything from mouse movements and voice patterns to typing rhythm and taps and swipes on a touchscreen. It’s challenging to mimic a user’s unique behavioral patterns, providing an additional layer of security.
8. Blockchain-based Verification
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing data storage and management by providing secure and tamper-resistant databases.
Storing and managing identity data on a decentralized blockchain increases transparency and privacy and ensures reliable recordkeeping.
9. Mobile-based Verification
This is considered an umbrella term for a wide range of convenient and frictionless identification methods via a user’s mobile device.
This would include the likes of using:
- One-time passwords (OTPs)
- Biometrics like fingerprint scanners or facial recognition
- QR code scanning
10. Social Media Authentication
This provides the convenience of getting access to websites and apps without the hassle of creating a new account. This approach allows users to use their current login details from social media accounts (such as Facebook or Instagram) to register and log into other websites. This method doesn’t need additional credentials and removes the cumbersome account creation steps.
11. Artificial Intelligence (AI) Verification
This falls under a broader category, involving various systems that use artificial intelligence methods to analyze data for precise identification and prevention of fraud. Automated identity verification enhances the authentication process of documents and user identities.
12. Location-based Verification
This approach involves verifying that a user’s reported location aligns accurately with their actual location. These systems use various methods to get a user’s location data, such as using Wi-Fi networks and GPS technology. For example, Facebook connects buyers with marketplace sellers that are local to minimize the risk of getting scammed.
Key Components of AI Identity Verification
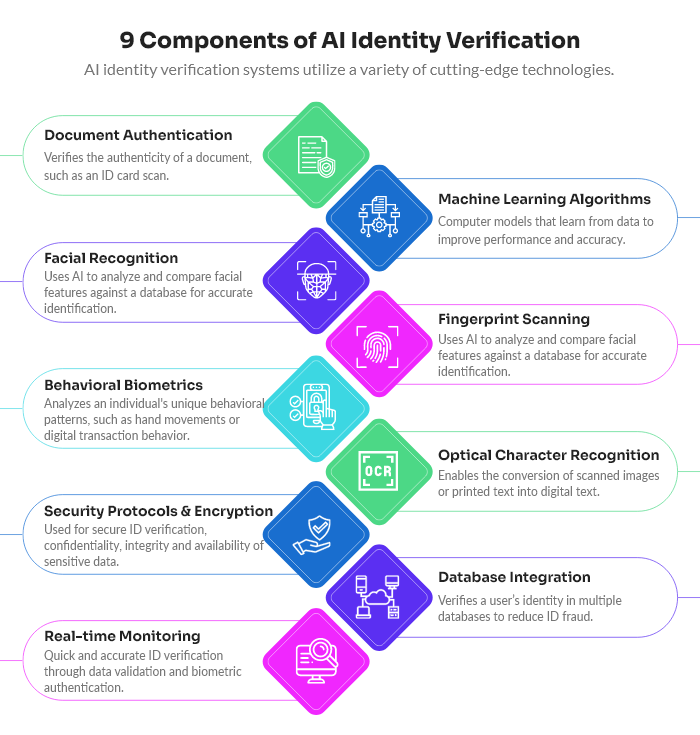
AI ID verification platforms rely on a variety of technologies and capabilities, including:
- Biometric Recognition – Biometric authentication is a process that uses the distinctive biological and behavioral traits of a user to automatically confirm their identity.
- Document Authentication – Document authentication involves confirming the legitimacy and authenticity of a document.
- Machine Learning Algorithms – AI algorithms monitor data to spot anomalies. These algorithms have the ability to continually learn and adjust using new data, allowing them to enhance their accuracy and effectiveness over time.
- Facial Recognition – Facial recognition systems scan and analyze a user’s photo. Using AI systems, these photos are cross-referenced against governmental ID photos.
- Fingerprint Scanning – Fingerprint tools scan an individual’s fingerprints. This is a highly sophisticated security protocol, and with AI it is highly accurate.
- Behavioral Biometrics – Behavioral biometric systems monitor a user’s transactions and online behavior. AI systems can use this
data to determine if something is out of the ordinary. - Optical Character Recognition (OCR) – OCR extracts and verifies information from various documents, including passports, driver’s licenses, and other forms of identification.
- Encryption – The latest AI verification platforms rely on encryption to protect user data stored in cloud databases.
- Database Integration – AI models rely on data; the more, the better. Therefore, integrating your business’s databases provides data to train and tune AI models specific to your needs.
Effortless ID Verification with AI!
Looking for a fast, accurate, and secure way to verify IDs? FTx Identity’s AI-Powered ID Verification solution is designed to help businesses of all sizes reduce fraud and streamline customer onboarding.
Benefits of AI in Identity Verification
Here are some of the ways that AI systems improve and enhance security for businesses:
Improved Accuracy and Speed
By integrating biometrics such as facial recognition, fingerprint scanners, and iris scanning, accuracy is enhanced, making it challenging for fraudsters to attempt spoofing.
AI efficiently manages high volumes of verification requests, leading to minimized wait times and streamlined processes.
Scalability and Cost-effectiveness
AI systems are good at handling a large amount of verification requests all at once, which makes them especially great for large-scale applications like ecommerce. This scalability ensures seamless onboarding and verification processes.
Automating processes not only saves money by reducing the need for manual review but also helps AI detect fraud more efficiently, minimizing losses from fraudulent activities.
Essentially, both aspects contribute to substantial cost savings.
Biometric Authentication
Biometric authentication eliminates the need for passwords and other less secure verification methods. It provides a more secure, faster, and reliable way to verify a user’s identity. It also uses artificial intelligence for enhanced fraud detection and prevention.
Anti-spoofing Technologies
There are different kinds of anti-spoofing technologies, including the following:
- Behavioral analysis
- Deepfake and synthetic identity fraud detection
- Liveness detection
- Multimodal verification
Anti-spoofing technologies make it much harder for fraudsters to gain access to a user’s private information.
Since fraud losses are reduced, there is no need to worry about expensive fraudulent activities.
Efficient Document Authentication
More and more, AI is used to check if documents are real. AI algorithms quickly look at documents for things like different fonts and security features. This helps eliminate the chance of fraud.
Continuous Monitoring and Behavioral Analysis
Identity verification with AI constantly checks data and user behavior in real-time for anything unusual. This involves keeping an eye on things like transaction patterns, login locations, and changes in biometric readings.
Behavioral analysis means studying how a user usually behaves to create a profile. It helps spot potential threats by looking out for odd login times and locations and sudden changes in activity.
Reduced Human Error
AI algorithms are great at processing large data sets and unique biometric features, like those in facial recognition, with more accuracy than humans. This reduces the risk of accidentally misidentifying someone.
Additionally, AI can continuously learn and adapt to new attack vectors. Therefore, it can detect sophisticated fraud attempts that a human might not be able to catch.
Quick Response Time
With AI-based identity verification, users don’t need to endure manual verification delays anymore. AI algorithms analyze biometric data, like facial features or fingerprints, directly on the device, eliminating the need for transferring data to remote servers.
Adaptability to Evolving Threats
Advanced AI systems can update their models automatically with the incorporation of new data and insights.
Because AI can analyze data in real-time, it can swiftly recognize and respond to emerging threats.
How AI Identity Verification Works
Identifying a user’s identity with AI creates a quick and convenient process.
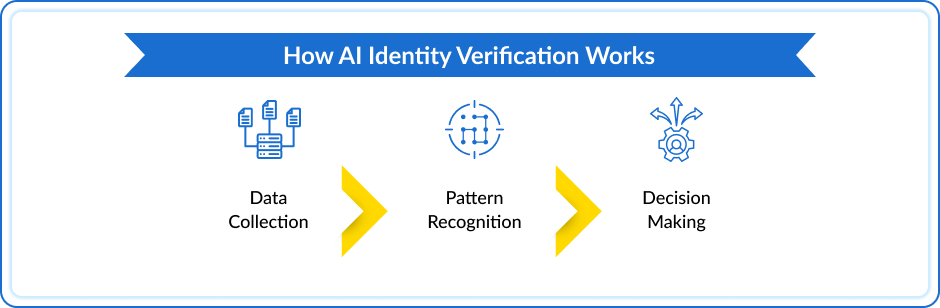
Here is a breakdown of what verification consists of:
Step-by-Step Process
Data Collection
First, information is required from the user. This might include:
- Biometric data: Facial features, fingerprints, and iris scans
- Document data: Official documents like passports or driver’s licenses
- Behavioral data: Typing patterns and mouse movements
Pattern Recognition
The collected data is then input into AI models, which have been trained on large datasets containing real and false identities. These models use sophisticated algorithms to perform the following:
- Identify features: Important characteristics are found in the data, such as specific facial points or voice pitch changes.
- Compare patterns: The features that have been extracted are compared against recognized patterns in the training data to recognize any similarities and discrepancies.
- Score the match: A numerical score is assigned, reflecting the degree of confidence in the match. Elevated scores mean there’s a greater likelihood of a genuine identity.
Decision Making
Based on the score obtained from the pattern recognition stage, the AI system reaches a decision:
- Verification approved: If the score is high enough, it confirms the user is who they say they are, and they get access.
- Verification Denied: If the score is too low, the system thinks something might seem suspicious, and it might deny access or ask the user for additional proof.
- Extra Check: Sometimes, the system might need more information, such as a video chat, to make sure it’s really the user.
Real-time Verification vs Batch Processing
| Feature | Real-time Verification | Batch Processing |
|---|---|---|
| Processing Speed | Instantaneous | Takes time for bulk processing |
| Response Time | Immediate feedback | Delayed results |
| Use Case | Suitable for quick verifications | Ideal for large data sets |
| Scalability | Well-suited for individual checks | Efficient for bulk verification |
| Resource Usage | Requires resources for immediate checks | Optimizes resources for bulk operations |
| Accuracy | Provides immediate and accurate results | Accuracy may vary based on batch complexity |
| Implementation | Ideal for scenarios requiring real-time decisions | Suited for scenarios where time is not a critical factor |
| System Load | Continuous demand on the system | Spreads demand over time |
| Cost Efficiency | May incur higher costs due to immediate processing | Often more cost-effective for large-scale verifications |
Let’s take a dive into the main differences between real-time verification and batch processing:
Real-time verification is a process that provides instant confirmation of a user’s identity using biometrics and digital identifiers.
Meanwhile, batch processing involves gathering and analyzing verification tasks collectively in groups, commonly referred to as batches, instead of handling them individually in real-time.
For real-time verification, as mentioned, identities are immediately verified. Getting verification results via batch processing is more time-consuming, which could result in delays.
The quick response of real-time verification helps minimize potential damage by immediately detecting and preventing fraud attempts. However, batch processing might not catch fraudulent activities occurring within the processing window.
Integration with Existing Systems
AI identity verification seamlessly integrates with existing systems through various methods, with a focus on achieving both seamless and secure data exchange. This includes the following:
Application Programming Interfaces (APIs): Numerous AI verification services provide APIs that establish direct connections with existing platforms, such as ecommerce businesses and banking systems. These APIs enable real-time data transfers and reduce the need for customized integrations.
Software Development Kits (SDKs): SDKs provide more access to the AI identity verification engine, allowing the creation of customized workflows and experiences within specific applications. Additionally, SDKs can facilitate the integration of advanced features such as liveness detection or multimodal verification directly into the existing system.
Accuracy and Reliability
As mentioned already, AI-powered identity verification holds promise for being faster and more convenient for businesses and customers alike.
Here are some major factors that contribute to its success:
Factors Influencing Accuracy
Quality of Training Data
How well AI models perform is linked to the kind and amount of data they learn from. Accurate identification greatly relies on having varied and good-quality datasets that effectively mirror the characteristics of the target population, particularly in terms of age, ethnicity, and gender.
Algorithm Sophistication
Selecting the right AI model structure and training method is important. For tasks such as image and video analysis, deep learning models like convolutional neural networks (CNNs) prove highly effective. Meanwhile, when dealing with sequential data like voice patterns, recurrent neural networks (RNNs) are considered the best choice.
Environmental Factors
It’s essential to pick the right biometric features for AI identification. Factors such as environmental conditions (i.e. low light, heavy makeup, or loud background noise) or temporary changes in appearance can impact the dependability of specific features.
Protect Your Business with AI-Driven ID Verification
Ensure compliance and reduce fraud risks effortlessly with FTx Identity’s intelligent ID verification software.
Use Cases of AI Identity Verification
AI-powered identity verification has a wide range of applications across multiple industries.

Some major use cases include the following:
Financial Institutions
Banking and Transactions: AI-driven identity verification is capable of authenticating users during both login and transactions. Also, the advantage of verifying identities quickly and securely makes the onboarding process go smoother.
KYC (Know Your Customer) Processes: Advanced algorithms in artificial intelligence can tell between genuine individuals and spoofing attempts. This prevents fraudulent account openings. When you get KYC verified online, The AI examines user data and transaction patterns in real-time to identify suspicious activities and potential fraudsters.
Ecommerce and Online Services
Account Registration: AI can use biometric data analysis to verify a shopper and prevent a fraudster from registering for a new account.
Fraud Prevention: By learning from previous situations with fraud, AI algorithms can predict the likelihood of future attempts. This allows businesses to take proactive measures to prevent fraudulent transactions before they happen.
Healthcare
Patient Verification: Facial recognition and other biometric methods ensure secure and accurate patient identification for remote consultations, healthcare facility entry, and access to electronic health records.
Prescription Authorization: To address concerns about prescription fraud and unauthorized access, patients can use biometrics for authentication and securely get their prescribed medications.
Common Challenges and Solutions
While AI identity verification certainly creates a quick and user-friendly experience and enhances security, there are some concerns surrounding it.
Privacy Concerns
AI-powered identity verification involves collecting a large amount of data. Due to that, it causes concerns about the possibility of privacy being invaded and data being misused.
There is also concern surrounding surveillance cameras with facial recognition capabilities in public spaces. There’s concern about it being potentially misused and the potential erosion of personal privacy.
Centralized databases are also vulnerable to cyberattacks, putting identity data at risk.
Addressing Data Security
AI-powered systems are vulnerable to cyberattacks, potentially exposing sensitive data to unauthorized actors.
Governments may demand access to AI identity verification data for security or other purposes, raising concerns about potential misuse and erosion of privacy rights.
A solution to this? Collect only the minimum necessary data, anonymize it where possible, and delete it securely after a defined retention period.
GDPR Compliance
It’s also important to implement and enforce strong data protection laws like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act).
This will ensure data privacy, transparency, and user control over their data.
Potential Bias and Fairness Issues
While AI-powered identity verification has been established as being convenient, quick, and user-friendly, concerns surrounding bias and fairness have come into the spotlight.
Biased data and algorithms have the potential to discriminate against specific groups based on factors such as race and gender. As a result, individuals may be denied essential services, leading to less trust in artificial intelligence.
To avoid this issue, it’s important to use a wide range of datasets during the AI model training process.
Also, using fairness-aware algorithms is essential.
Finally, consistent auditing and monitoring should be enforced to detect and address any potential bias that may occur.
Future Trends in AI Identity Verification
You can look forward to some pretty cool improvements in how AI checks identities in the future.
Here are a few examples:
Advancements in Machine Learning
Biometrics is set to advance beyond just recognizing faces. More people are likely to use a variety of biometric methods, such as voice, walking style, eye scans, and even vain patterns.
Advanced machine learning models will not only compare pictures but also identify fake attempts by analyzing subtle facial expressions, involuntary movements, and even blood flow.
Emerging Technologies in Biometrics
As we use biometrics more, keeping our data private becomes crucial. Technologies that boost privacy, such as federated learning and secure enclaves, will become more popular. These technologies let AI models learn from data without seeing the data directly.
Regulatory Changes and Impacts
You can expect the extension and stricter enforcement of data protection laws such as GDPR and CCPA. This especially applies to AI-powered identity verification systems. This expansion will offer explicit rules regarding how data is collected, stored, utilized, and deleted. This will give users more control over their personal information.
To make it easy and safe for your identity check with different companies, rules might encourage using the same data formats and rules. This way, users can share their confirmed identity with different services without going through so many verification steps each time.
Fighting Against Identity Fraud with FTx Identity
With the advancement of artificial technology, we are entering a new era of combating the constant issue of identity fraud.
No single solution is going to be enough.
However, AI shows great potential when it comes to detecting and fighting back against identity thieves.
We must find a way to make use of these tools and create a comprehensive approach for keeping identities secure. By using these tools, we are one step ahead of identity fraud.
To learn more about what FTx Identity can do for your business, be sure to set up a consultation with us today and check out a demo!
Ready to enhance your security and customer experience with AI-powered ID verification?
Contact us today to schedule a demo and see how FTx Identity can transform your age verification process.
Fill out the form to get started!
