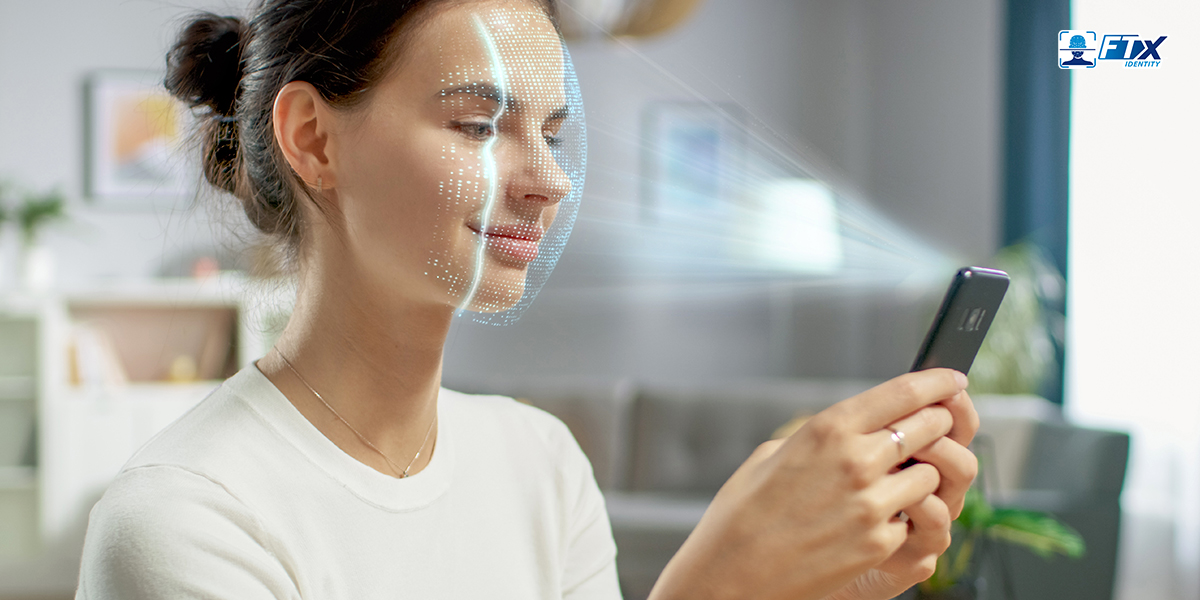
One in 3 Americans have been the victim of identity theft, and often, stolen identity data is used to commit identity fraud, according to Proofpoint, Inc.
Businesses can protect themselves by implementing advanced verification solutions, known as identity proofing platforms, to confirm an individual’s identity. Identity proofing is one of the most comprehensive forms of customer verification, and it goes beyond simple ID checking.
With identity proofing, an individual must:
1. Establish that the identity belongs to a real-life person,
2. Prove that they are, in fact, the same person as the validated identity,
3. And that you are physically present during the process.
Table of Contents:
- What Is Identity Proofing?
- Identity Proofing vs. Identity Verifications
- Why Is Identity Proofing Important?
- How Can Companies Implement Identity Proofing?
- Challenges and Considerations in Identity Proofing
- Use Cases of Identity Proofing
- Emerging Trends in Identity Proofing
According to Fortune Business Insights, the global identity verification market was valued at $10.45 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to rise from $11.97 billion in 2024 to $39.82 billion by 2032.
Identity proofing has become a cornerstone of trust and security in the digital age. That’s why it is important for businesses to go with a service provider that has it all! Get in touch to understand how you can start protecting your business today.
In the past, identity proofing was simple. For example, if you ever opened a bank account, you likely went through an identity proofing process. You provided multiple forms of ID (e.g., a driver’s license, social security card, and proof of address). And the bank teller would verify your credentials and cross-check your ID.
However, with many transactions moving online, identity proofing methods have had to evolve.
Remote identity proofing occurs online, and it requires advanced technology to determine if an individual is present and if they do exist in real life. Ultimately, whether done face-to-face or online, identity proofing is an important tool for combatting identity fraud.
This guide covers the basics, including what identity proofing is, how it works, and why businesses need it to address modern threats.
What Is Identity Proofing?
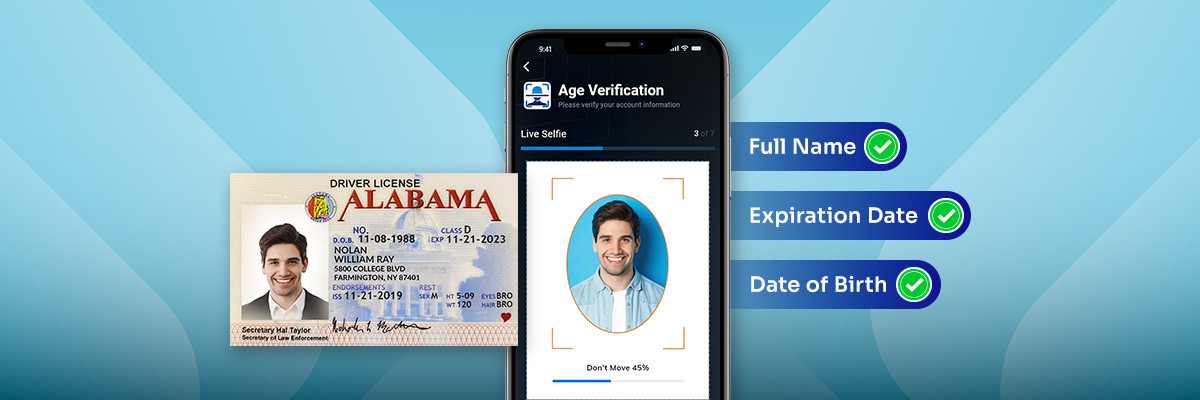
The Computer Security Resource Center from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) defines identity proofing as the process of providing sufficient information (e.g., identity history, credentials, documents) to establish an identity.
However, typically identity proofing goes much deeper. In fact, according to Gartner’s Identity Verification and Authentication Market Report document-centric identity proofing is now recommended. In document-centric identity proofing, a customer:
Provides a government-issued ID or multiple forms of ID by taking and uploading a photo.
The validity of the identity document is determined, typically by cross-referencing with public data (like DMV records or credit bureau data).
Finally, the user must take a selfie, where liveness detection validates their real-time presence. This determines if the user is present and prevents spoofing attempts or deepfake fraud.
Therefore, in essence, identity proofing aims to prove the identity of an individual with a higher degree of certainty. Simple age verification or ID verification processes likely don’t include liveness detection or require multiple forms of ID.
Identity Proofing vs. Identity Verifications
Identity proofing and identity verification often get used interchangeably. But they represent distinct phases of the ID confirmation process.
Identity proofing, for example, refers to the entire process of establishing and proving a customer’s identity. Identity verification, however, refers to only the cross-referencing of customer-provided data against authoritative sources like a governmental database.
In short, you can’t perform identity proofing without identity verification.
A Real-Life Example
Suppose you were checking into a hotel. You’re required to provide an ID document. The hotel clerk will perform identity verification to ensure your ID document is valid and will ask for you to supply the card on file. After reviewing your ID and payment details, the clerk will have successfully proven your identity.
Why Is Identity Proofing Important?

Identity proofing plays a pivotal role in modern verification. Here are some of the key benefits:
1. Secure Customer Onboarding
From ecommerce platforms to financial institutions, businesses often require customers to provide personal information during the onboarding process.
Identity proofing serves as the first line of defense, ensuring that these customers are legitimate and are not engaging in identity fraud or theft. By meticulously verifying customer identities, businesses can establish a foundation of trust and preemptively thwart potential fraudulent endeavors.
2. Fraud Prevention
Identity fraud poses a significant threat to businesses, leading to substantial financial losses. Document-centric identity proofing acts as a potent deterrent, helping to prevent the use of fabricated identities.
Companies can prevent stolen identity data from being used through liveness selfie verification.
Using robust verification to establish that the identity is, in fact, real.
3. Ensuring Regulatory Compliance
Many industries have stringent KYC protocols. With identity proofing, companies can strengthen their due diligence practices, ensuring they adhere to rigorous industry regulations
4. Faster Onboarding
Identity proofing isn’t solely focused on security; it also contributes to a streamlined user experience.
By optimizing the verification process, businesses can reduce friction for genuine users while maintaining robust security measures. Striking this balance is particularly crucial in the fast-paced digital landscape of today.
How Does Identity Proofing Work?
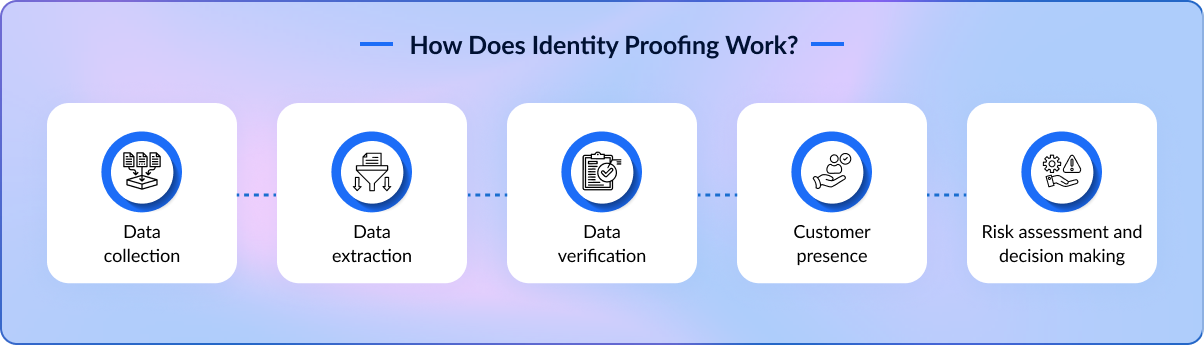
The identity proofing process is straightforward. However, it relies on advanced technology to verify authenticity. Here’s how the process works:
1. Data Collection – A customer provides identifying documents like a driver’s license or passport. They may also be required to submit other identifying documents like a social security card, proof of address, or a credit card.
2. Data Extraction – A tool like ICR (intelligent character recognition) extracts the data from the document and puts it into a readable format.
3. Data Verification – Advanced systems cross-reference the data with established databases. This ensures the identity is that of a real person.
4. Customer Presence – A live selfie is used to cross-reference the ID photo and ensure liveness detection. This establishes that the individual is present and matches the identity on the ID document.
5. Risk Assessment and Decision Making – ID proofing systems assess the authenticity. A high-risk transaction, for example, may require higher levels of matching, compared to a lower-risk transaction. Ultimately, a decision is made and the identity is proved.
How Can Companies Implement Identity Proofing?

Identity proofing is a process to confirm someone’s identity before giving them the right to access sensitive resources or information. Identity proofing isn’t a new concept, but it has gained traction in recent years. The rise of digital transactions has made it simpler for people to create and hold accounts, and the expansion of data breaches has made it more important than ever.
To implement identity proofing, this layered approach should be taken by companies:
1. Identify the Threats
The first clear-cut step in any identity proofing program is to figure out what sort of data needs to be protected and from whom. It is mandatory for companies to analyze potential attack vectors such as phishing, social engineering, and data breaches. Assess the potential financial, legal, and reputational consequences of identity fraud.
2. Review Internal Controls
The second step would be to review your existing processes and controls. Companies should start identifying and addressing gaps in the current system. Along with these, implement strong password policies, multi-factor authentication, and role-based access control. Create and maintain a plan for responding to fraudulent activities. Educate employees about fraud risks and best practices for identity verification.
3. Assess External Controls
Regarding identity proofing, just reviewing your system isn’t enough. You must assess your vendor’s policies, controls, and procedures. You’ll have to ensure you have standard procedures and policies that clearly state how you’ll stop security breaches and fraud while confirming the correct response if the breach occurs.
Challenges and Considerations in Identity Proofing
While identity proofing offers an array of benefits, these systems do have shortcomings. For example, identity proofing requires a variety of Personally Identifying Information (PII) to be shared. Without robust security and strict data storage protocols, this data increases the risk for identity theft.
Here are some of the potential risks of identity proofing:
1. Privacy Concerns
The collection and storage of personal information inevitably raises privacy concerns. Businesses must meticulously navigate the fine line between obtaining the necessary data for identity proofing and respecting users’ privacy rights.
Businesses also need to establish clear data storage protocols, including which PII is stored and how long it is.
2. False Positives and Negatives
No system is entirely immune to errors, and identity proofing may occasionally result in false positives (incorrectly identifying a legitimate user as fraudulent) or false negatives (failing to identify fraudulent activity).

Fortunately, many of these systems get stronger and more reliable as you add data to the model. Therefore, when initially launching a program, you should incorporate spot checks and tune risk scoring to counterbalance this potential.
3. Evolving Threat Landscape
As technology advances, so do the tactics employed by cybercriminals. Identity proofing processes must remain agile to keep pace with emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
Some of the most common include:
- Deepfake fraud
- Synthetic identity fraud
- AI-based security fraud
Choose a platform that incorporates constantly updated technology to address the latest threats.
Use Cases of Identity Proofing
Identity proofing plays a crucial role in establishing trust and security across various sectors. Here’s a breakdown of key use cases:
1. Sharing Economy Platforms
Sharing economy platforms, like ride-sharing, home-sharing, and peer-to-peer marketplaces, rely heavily on identity verification. Identity proofing helps:
- Enhance Trust and Safety: Verifying the identity of users builds trust and reduces the risk of fraudulent or malicious activity.
- Prevent Fraud: Identity proofing helps prevent fake profiles, stolen credentials, and other forms of fraud.
- Ensure Accountability: Holding users accountable for their actions fosters a safer and more reliable platform experience.
- Compliance with Regulations: Some jurisdictions require platforms to verify user identities for regulatory compliance.

2. Cryptocurrency Exchanges
Cryptocurrency exchanges face significant risks related to fraud and money laundering. Identity proofing is essential for:
- Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) Compliance: Exchanges are legally obligated to verify user identities to comply with KYC and AML regulations.
- Preventing Account Takeover: Strong identity verification reduces the risk of unauthorized access to user accounts.
- Combating Fraudulent Transactions: Identity proofing helps detect and prevent fraudulent transactions, such as using stolen credit cards or fake IDs.
- Building Trust and Security: Verifying user identities enhances the exchange’s reputation and builds trust among users.
3. Telecommunication Companies
Telecommunication companies use identity proofing for various purposes, including:
- Preventing SIM Swap Fraud: Verifying the identity of customers before issuing SIM cards helps prevent SIM swap fraud.
- Account Activation and Management: Identity proofing is used to verify the identity of customers when activating new accounts or making changes to existing ones.
- Compliance with Regulations: Some jurisdictions require telecommunication companies to verify customer identities for regulatory compliance.
- Reducing Fraudulent Activities: Prevents activities like fraudulent account creation and service misuse.
4. Legal Service Providers

Legal service providers handle sensitive client information and require robust identity proofing to:
- Protect Client Confidentiality: Verifying client identities helps protect sensitive information and maintain confidentiality.
- Prevent Impersonation: Identity proofing helps prevent impersonation and ensures that legal services are provided to the rightful client.
- Comply with Regulatory Requirements: Legal professionals are often subject to strict regulations regarding client identification and verification.
- Secure Remote Legal Services: With the rise of remote legal consultations, identity proofing is crucial for verifying client identities securely.
5. Financial Institutions
Financial institutions, including banks, credit unions, and investment firms, are heavily regulated and face significant risks related to fraud and money laundering. Identity proofing is critical for:
- Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) Compliance: Financial institutions are legally required to verify customer identities to comply with KYC and AML regulations.
- Preventing Account Fraud: Identity proofing helps prevent fraudulent account openings and unauthorized access to existing accounts.
- Reducing Credit Card Fraud: Verifying customer identities during credit card applications and transactions helps reduce fraud.
- Secure Online Banking and Mobile Payments: Identity proofing is essential for secure online banking and mobile payment transactions.
- Mortgage and Loan Applications: Rigorous identity verification is a part of the lending process to prevent fraud and ensure the applicant is who they say they are.
Emerging Trends in Identity Proofing
Verifying your identity online used to be a one-time thing, like showing your ID to open a bank account. But the fight against fraudsters is getting more sophisticated, and so is identity proofing.
Gone are the days of a single verification. Generally, identity proofing systems require multiple verifications (at set intervals) and incorporate behavioral biometrics to monitor for fraud in real-time.
Here are some of the key trends in the industry:
Continuous Identity Proofing: Forget a single snapshot. This approach constantly monitors your activity, like login attempts and spending habits. If something suspicious pops up, like a login from a new country, the system can spring into action and potentially block fraud in real-time by asking the user to reverify.
Your Identity, Your Way with Blockchain: Blockchain technology, known for its tamper-proof nature, could make user-controlled verification possible in the future. With blockchain, you could choose what data to share with different entities, keeping your personal information under your own lock and key.
AI and Machine Learning: Artificial intelligence and machine learning continually evolve and get stronger. Many systems incorporate these tools throughout the process. For example, OCR and ICR extract data from an ID document, while facial recognition is used in selfie identity verifications. Additionally, behavioral biometric and fraud detection systems leverage the power of AI to prevent fraud in real-time.

These trends are paving the way for a future where security and convenience go hand-in-hand. With continuous monitoring, secure data storage, and AI-powered tools, verifying your identity online will be safer and smoother than ever before.
Recap: Identity Proofing Is a Best Practice
There are a variety of verification solutions on the market and each offering a different level of verification. Identity proofing, however, stands out at the top of the market. Its advanced verification techniques make this the gold standard for high-risk transactions, in KYC processes, and for performing enhanced due diligence.
Although it may be too robust for some situations, even a pared-down version that includes selfie verification will help you build trust with customers while preventing malicious actors from committing fraud. Does your business need an identity verification solution?
Avoid falling for digital identity traps and make your business foolproof with FTx Identity!
