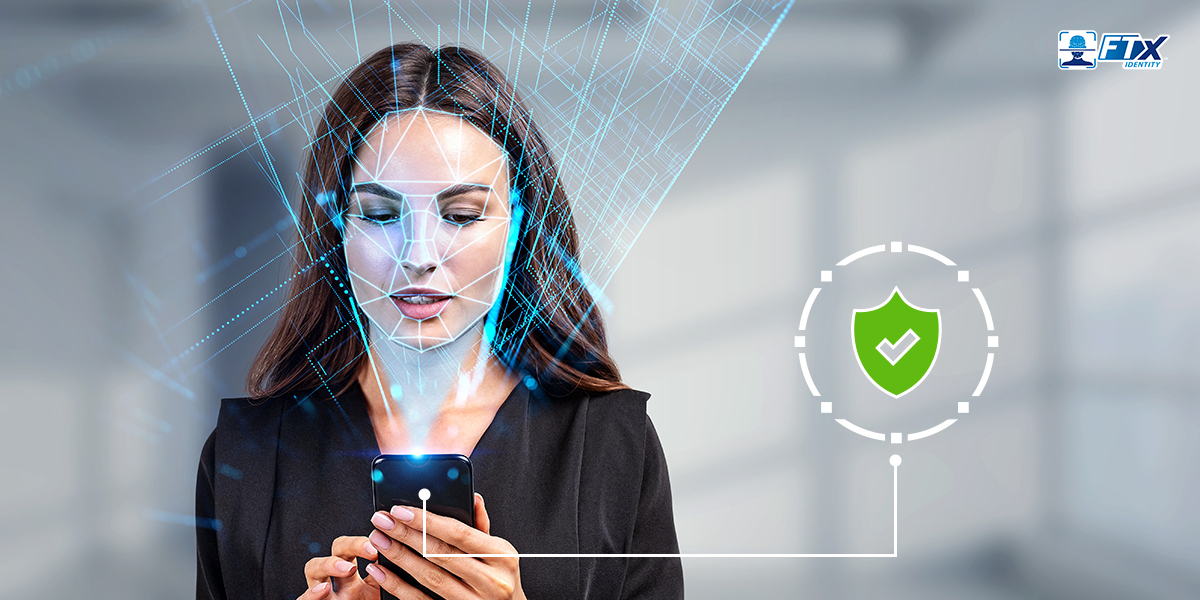
The Rising Stakes of Fintech Identity Fraud:
As digital banking, crypto, and payment apps explode, so do risks. Synthetic identities, deepfakes, and account takeovers are slipping through outdated verification systems.
The stakes?
Regulatory penalties, lost customer trust, and millions in fraud losses.
As quoted in Forbes, “Alloy’s 2023 State of Compliance report found that 93% of fintech companies struggle to meet compliance standards, and 60% of surveyed companies paid over $250,000 in compliance fines in the past year. ”
Another from FinTech Global stated, “ 2024 has been a watershed year for regulatory enforcement, marked by a dramatic increase in global fines that reached an unparalleled $19.3bn. ”
That’s why bulletproof identity verification isn’t optional anymore – it’s fintech’s frontline defense. From AI-driven biometric checks to real-time document scanning, next-gen identity verification solutions are helping fintech companies balance security, compliance, and seamless user experience.
Let’s break down why fintechs can’t afford to cut corners on ID verification – and how to get it right.

Traditional Methods of Verifying Identity in Fintech – And Why They Fail Today
For decades, banks and financial institutions relied on manual, in-person identity checks –think paperwork, long queues, and face-to-face interviews. But in today’s digital-first fintech world, these legacy methods are slow, insecure, and painfully outdated.
The Old Way: Manual KYC & In-Person Onboarding
Legacy verification typically involved:
– Physical document checks (passports, utility bills) handed over at a branch.
– Scanned ID uploads with no real-time validation, leaving room for forged documents.
– Offline background checks, dragging onboarding from days to weeks.
While this worked when banking was branch-bound, digital fintech demands speed and security – something manual processes can’t deliver.
Why Traditional Methods Don’t Cut It Anymore
1. No Scalability
– Manual reviews bottleneck growth – imagine verifying 10,000 users with paper forms!
– Fintechs lose customers to faster competitors during delays
2. Fraud Vulnerabilities
– Photoshopped IDs slip through unchecked
– No liveness detection means fraudsters reuse stolen selfies
3. Regulatory Risks
– Human errors in KYC lead to compliance gaps (and hefty fines)
– General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and AML laws now demand real-time, auditable proof – not paper trails
The Fallout: Lost Customers & Compliance Breaches
It was found in an account opening study provided by MX that 68% of users give up on online financial applications when the process feels too complicated or takes too long to verify (for example, taking >5 minutes).

Also, fraud starting with fake IDs happens because legacy systems lack AI-powered fraud detection.
The bottom line?
Fintechs stuck in the “scan-and-wait” era risk fraud, fines, and frustrated users.
The fix?
Next-gen identity verification – like FTx Identity – that combines biometrics, AI, and instant checks to secure onboarding without friction.
Challenges with Traditional Methods
Why Is Legacy Identity Verification Failing Fintech?
Fintech thrives on speed, security, and seamless UX – yet traditional identity verification methods drag it down with inefficiency, risk, and frustration.
Here’s why outdated systems are costing Fintech customers, compliance, and revenue:
Slow Onboarding = Lost Customers
Why It Hurts
Manual reviews mean days of delays – while digital-native users expect instant. On the contrary, competitors with instant verification (like biometric checks) steal your potential customers.
The Solution
FTx Identity offers AI-powered verification that reduces the identity verification to under 30 seconds, keeping users engaged.
Inconsistent Compliance Across Borders
Problem: A fintech operating in the US, EU, and Asia faces:
- Different KYC/AML rules per region.
- Patchwork document requirements (e.g., a German ID vs. a Japanese My Number card).
- Result: Manual processes fail audits, trigger fines, and block expansion.
How FTx Identity fixes it:
– Global ID coverage (180+ countries)
– Auto-updates for changing regulations
The Hidden Costs of Human Error
1. Fraud risk: Manual checks miss:
– Deepfake videos
– AI-generated synthetic IDs
2. Compliance fines: Most fintech penalties stem from KYC oversights
3. Operational costs: Hiring teams to review IDs is undoubtedly pricier than automated systems
FTx Identity’s advantage:
– AI fraud detection flags suspicious patterns
– Biometric liveness tests stop impersonators
Legacy verification slows growth, increases fraud, and drains resources. Fintechs need smarter tools – like FTx Identity’s AI-driven platform – to:
- Prevent abandonment with lightning-fast checks
- Stay globally compliant without manual headaches
- Cut costs by reducing human reviews
Next-gen verification isn’t just better – it’s non-negotiable.
Transition to Digital: What Changed?
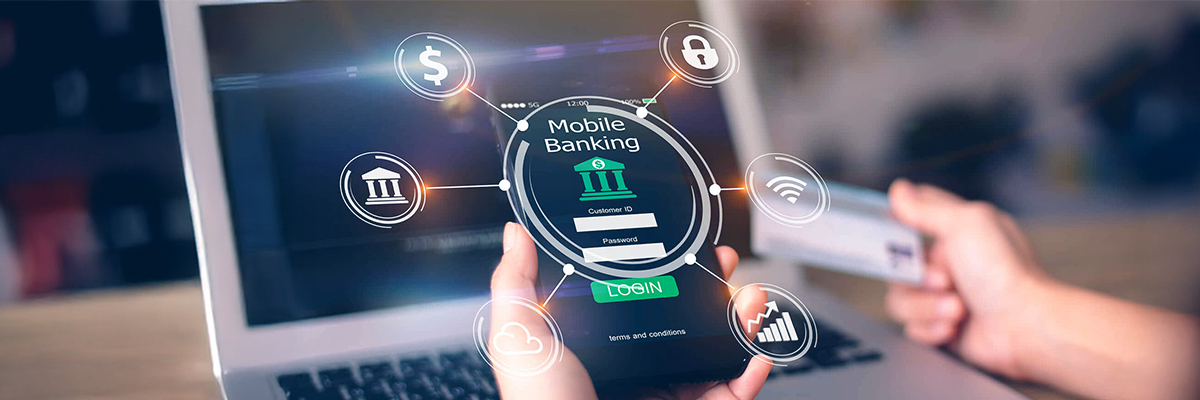

The Digital Shift: What Changed in Fintech Identity Verification?
The financial sector underwent a radical transformation as traditional verification methods became incompatible with modern demands.
Three key forces drove fintech to adopt digital identity solutions:
1. Mobile-First Banking Changed User Expectations
– Customers now demand instant access to financial services from their smartphones, rejecting slow, paper-based processes.
– The rise of neo-banks set new standards – users expect onboarding in minutes, not days.
– Financial institutions that relied on manual verification lost customers to competitors offering seamless digital experiences.
2. Regulatory Demands Outpaced Manual Processes
– As fintech expanded globally, compliance requirements became more complex across different jurisdictions.
– Traditional KYC methods couldn’t efficiently handle increasing user volumes while maintaining audit trails.
– Regulators began expecting real-time monitoring and automated reporting, impossible with legacy systems.
3. Surging Digital Fraud Required Stronger Defenses
– Cybercriminals developed sophisticated attacks like AI-generated fake IDs and deepfake spoofing.
– Static verification methods failed to detect these evolving threats, leading to account takeovers and synthetic identity fraud.
– Financial institutions needed dynamic solutions that could adapt to new fraud patterns instantly.
What Is Fintech Identity Verification? (KYC, AML, KYB)
Fintech identity verification isn’t just about checking IDs – it’s a regulatory shield and fraud-fighting tool built for digital finance.
Unlike generic solutions, fintech verification must:
– Comply with strict financial regulations (KYC, AML, KYB).
– Stop sophisticated fraud (synthetic identities, deepfakes).
– Scale instantly for global user bases.
The Fintech Verification Framework:
1. KYC (Know Your Customer)
– Fintech twist: Not just collecting IDs – but AI-powered validation in seconds.
– Used for: Onboarding users while blocking fraudsters.
2. AML (Anti-Money Laundering)
– Fintech twist: Real-time transaction monitoring + behavioral analytics to spot laundering.
– Used for: Flagging suspicious activity (e.g., crypto tumbler transactions).
3. KYB (Know Your Business)
– Fintech twist: Automated corporate ownership checks to prevent shell companies.
– Used for: Merchant onboarding (e.g., payment processors).
Technologies Powering Fintech Identity Verification
Fintech doesn’t just adopt tech – it pushes it further.
Here’s what makes modern verification fast, accurate, and fraud-proof:
1. AI & Machine Learning
– Does: Analyzes thousands of data points (ID fonts, facial micro-expressions) to catch fakes.
– Fintech edge: Learns from new fraud patterns in real-time (e.g., spotting AI-generated IDs).
2. Liveness Detection + Facial Recognition

– Does: Confirms the user is real and present (not a photo or deepfake).
– Fintech edge: Uses 3D depth mapping to thwart even advanced spoofs.
3. OCR (Optical Character Recognition)
– Does: Instantly extract data from various ID types globally.
– Fintech edge: Auto-fills forms and cross-checks against sanctions lists.
4. Biometric & Behavioral Analytics
– Does: Verifies via voice and eyes.
– Fintech edge: Continuous authentication after onboarding (e.g., detecting account takeovers).
Digital Methods of Identity Verification
Modern Digital Identity Verification in Fintech
Fintechs now deploy multi-layered verification ecosystems, combining cutting-edge technologies to combat fraud while ensuring seamless user experiences.
Here’s a streamlined breakdown of the most effective methods:
1. Knowledge-Based Verification (KBV)
Users answer dynamic, personalized questions based on credit history or records, adding an extra security layer for high-risk transactions while preventing social engineering bypass.
2. Biometric Authentication
Facial recognition creates a lasting digital identity that helps prevent account takeovers, ensures seamless transaction approvals, and safeguards against session hijacking even after you’ve logged in.
3. Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Evolved 2FA uses push notifications with biometric confirmation, balancing security with minimal friction for adaptive risk-based access.
4. Digital ID Verification
Leverages government-issued digital IDs or bank-verified identities to enable instant, cross-border onboarding with built-in compliance.
5. Blockchain-Based Verification
Self-sovereign identities and immutable audit trails let users control data while simplifying KYC reuse and reducing PII storage – ideal for crypto/DeFi platforms.
6. Machine-Readable Zone (MRZ) Scanning
Multi-angle MRZ scanning decodes passports/IDs with 99.9% accuracy, even when damaged, and cross-checks global watchlists offline for remote areas.
7. Selfie ID Checks
AI-powered liveness detection compares real-time selfies with ID photos, preventing deepfake spoofing while meeting strict KYC compliance requirements in seconds.
8. Mobile Document Capture
Smartphone-enabled OCR scans and instantly validates various ID types, detecting sophisticated forgeries through tamper-proof font analysis, hologram spectral analysis, microprint verification, and UV/IR detection to expose professional forgeries that basic OCR misses.
9. SSN & Credit Bureau Verification
Real-time cross-referencing with government and financial databases exposes synthetic identities by flagging mismatched personal/credit histories.
10. IP/Geolocation Risk Scoring
Behavioral AI analyzes network patterns to automatically block suspicious cross-border logins and bot-driven credential stuffing attacks.
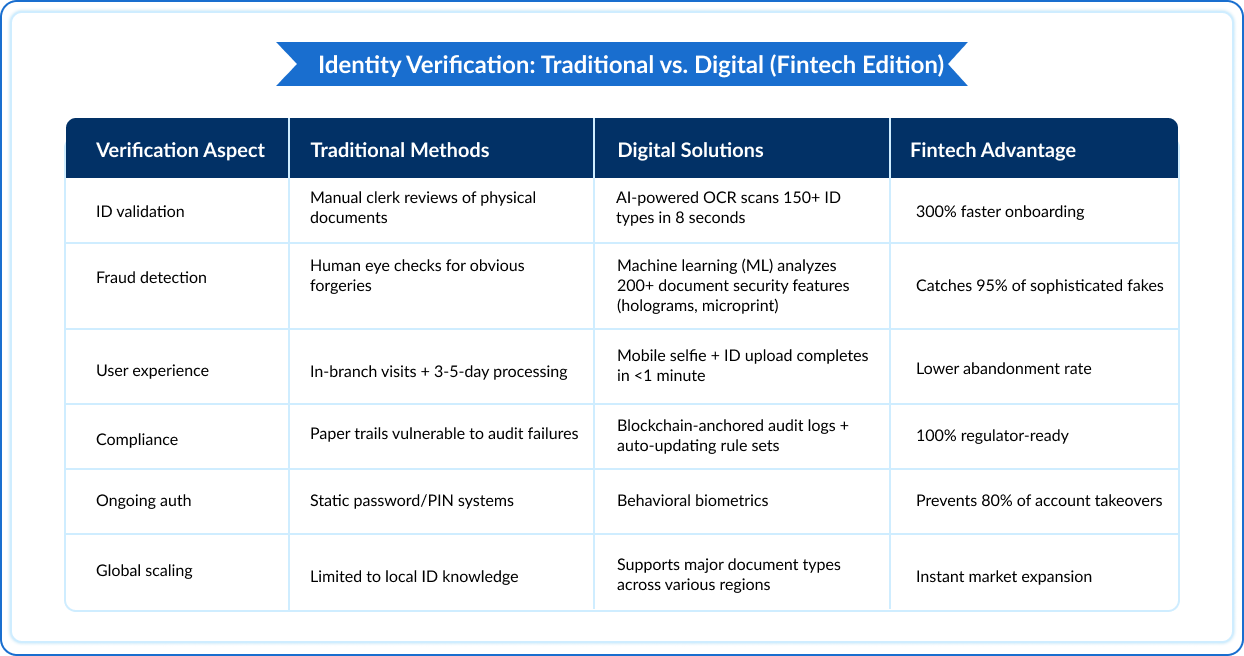
Take a quick look at the difference between traditional and digital verification methods:
Identity Verification: Traditional vs. Digital (Fintech Edition)
Must-Have Features in a Fintech Identity Verification Solution
Fintech companies operate in a highly regulated environment where security, compliance, and user experience must work together. A robust identity verification solution is no longer optional – it’s critical for preventing fraud, meeting regulatory requirements, and delivering seamless customer onboarding.
Here are the 9 essential features every fintech identity verification system needs:
1. Compliant with Local Requirements
Fintechs must follow strict KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (Anti-Money Laundering) regulations that vary by country. A strong verification solution should:
– Automatically adapt to regional compliance rules (e.g., GDPR in Europe, FinCEN in the US).
– Support multiple government-issued ID types (passports, driver’s licenses, national IDs).
– Ensure data privacy with encryption and secure storage.
2. Fraud Resistant
Traditional verification methods fail against modern fraud tactics like deepfakes, synthetic identities, and document tampering. A fraud-resistant system must include:
– Biometric authentication (facial recognition, liveness detection).
– AI-powered document verification to detect forged IDs.
3. Customer-Centric
A slow or complicated verification process leads to user drop-offs. A customer-friendly solution should:
– Verify identities in under 30 seconds (vs. days with manual checks).
– Offer mobile-friendly onboarding (selfie + ID upload in one step).
– Allow reusable digital identities to avoid repeated KYC checks.
4. Technically Sustainable
Fintechs need a system that scales with growth without performance issues. Key requirements:
– Cloud-based infrastructure for high-volume verifications.
– Low-latency processing (<1 second response time).
– 99.9% uptime to prevent disruptions during peak traffic.
5. Real-Time Risk Assessment
Waiting for manual fraud checks is outdated. A modern system should:
– Instantly score risk based on behavior, device, and location.
– Trigger additional checks for suspicious activity.
– Continuously monitor for account takeovers post-onboarding.
6. Sanctions & PEP List Screening
Fintechs must screen users against global watchlists to avoid legal risks. A reliable system should:
– Scan sanctions lists (OFAC, UN, EU) in real-time.
– Flag Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs) for enhanced due diligence.
– Auto-update lists to stay compliant.
7. Cross-Device & Geolocation Checks
Fraudsters use VPNs, emulators, and stolen devices to bypass security. A strong system must:
– Detect spoofed locations (mismatched IP addresses).
– Block suspicious devices (rooted/jailbroken phones).
8. Audit Trail Generation
Regulators require transparent KYC processes. A compliance-ready system should:
– Log every verification attempt (timestamp, method, result).
– Store encrypted records for easy audits.
– Generate compliance reports in one click.
9. API-First & Modular Integration

Fintechs need flexible, plug-and-play solutions – not rigid systems.
The best platforms offer:
– RESTful APIs for easy integration with banking apps, ecommerce, and more.
– SDKs for mobile/web to embed biometric authentication.
– No-code options for quick deployment.
Compliance Landscape in Fintech
Regional Compliance Breakdown: How ID Verification Meets Global Fintech Regulations
Fintech companies operate across borders, making compliance with region-specific regulations critical. A robust identity verification solution helps meet these requirements while preventing fraud and financial crimes. Here’s how KYC, AML, and data privacy laws vary across key markets—and why digital ID verification is essential.
1. United States: FinCEN, BSA & Strict AML Enforcement
The U.S. has some of the toughest AML (Anti-Money Laundering) laws, enforced by the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN). Key regulations include:
– Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) – Requires reporting cash transactions over $10,000 and suspicious activity.
– Customer Due Diligence (CDD) Rule – Mandates verifying beneficial ownership for business accounts.
– FinCEN’s 2024 Crypto Rules – Crypto firms must now comply with BSA reporting.
How ID Verification Helps
– Automates KYC checks to meet FinCEN’s real-time reporting demands.
– Flags high-risk users (PEPs, sanctioned entities) before onboarding.
2. European Union: GDPR, 6AMLD & Digital Identity Wallets
The EU’s strict data privacy (GDPR) and anti-fraud (6AMLD – The Sixth Anti-Money Laundering Directive) rules require:
– Explicit user consent for data processing.
– Stronger biometric verification under eIDAS 2.0 (Digital Identity Wallets).
– Stricter AML reporting – failure to file can lead to 4% global revenue fines.
How ID Verification Helps?
– Encrypts personal data to meet GDPR standards.
– Supports eIDAS-compliant digital IDs for cross-border fintech services.
– Prevents fines like Danske Bank’s $2B penalty for AML failures.
3. APAC: Diverse KYC Laws & Rising Fraud Threats
Asia-Pacific has fragmented regulations, with strict rules in:
– Singapore (MAS KYC Guidelines) – Mandates video verification for high-risk accounts.
– India (RBI’s Aadhaar eKYC) – Allows biometric authentication via national ID.
– Australia (AUSTRAC AML/CTF Act) – Requires real-time transaction monitoring.
How ID Verification Helps?
– Adapts to local ID types (Aadhaar, MyKad, Japan’s My Number).
– Detects synthetic identity fraud
4. FATF’s Global AML Standards & Why They Matter
The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) sets international AML guidelines, requiring:
– Risk-based KYC approaches (higher checks for crypto, cross-border payments).
– Sanctions/PEP screening across 190+ countries.
– Audit trails proving compliance for 5+ years.
How ID Verification Helps?
– Auto-updates sanctions lists (OFAC, UN, EU).
– Generates blockchain-backed audit logs for FATF inspections.
Risks of Weak Identity Verification in Fintech
1. Increased Fraud and Chargebacks
Weak verification systems fail to stop modern fraud tactics like synthetic identities and account takeovers. Without proper checks, fintechs face mounting financial losses from fraudulent transactions and costly chargebacks that directly impact profitability.
2. Regulatory Penalties
Financial authorities impose heavy fines for compliance failures in KYC/AML processes. Inadequate identity verification leads to violations of evolving global regulations, resulting in multimillion-dollar penalties and increased regulatory scrutiny.
3. Customer Churn Due to Friction
Complex or slow verification drives users away during onboarding. Today’s customers expect instant access, and clunky authentication processes cause significant drop-offs, hurting customer acquisition and growth.
4. Poor Investor/Partner Trust
Repeated fraud incidents or compliance breaches damage credibility with investors and banking partners. Weak verification systems raise red flags during due diligence, limiting funding opportunities and strategic partnerships.
5. Operational Inefficiencies
Manual verification processes are costly and unscalable. Legacy systems require excessive resources to maintain compliance, creating bottlenecks that hinder business expansion and innovation.
Strategic Steps for Risk Mitigation
- Deploy multimodal authentication combining biometrics, behavioral analysis, and document verification
- Implement real-time risk scoring that adapts to emerging fraud patterns
- Automate compliance workflows to maintain audit-ready documentation
- Prioritize user experience without compromising security thresholds
Importance of Identity Verification in Fintech’s Growth & Trust
Getting identity verification right is tricky – too strict and you frustrate users, too lax and you invite fraud. But modern solutions finally deliver both security AND smooth experiences. Here’s why that matters more than ever:
Customers Actually Want Strong Verification
– According to FinTech Futures, 74% of users see physical biometrics as the most trustworthy security
– PIN codes remain the second most preferred method (showing users value layered security)
– The biometrics market is projected to hit $173.08B by 2033 (imarc) – proof this isn’t just a compliance checkbox
The Business Growth Benefits
Powerful verification does more than prevent fraud – it:
– Builds instant trust during onboarding (critical when users can’t “see” your physical branch)
– Creates competitive advantages over slower, traditional banks
– Unlocks global expansion by handling regional compliance automatically
Future-Proofing Your Fintech
As digital finance grows, so will:
– Regulatory demands (especially for crypto and cross-border payments)
– User expectations for frictionless security
– Fraud sophistication (deepfakes, synthetic IDs)
The fintechs winning tomorrow are those investing in verification today – not just to survive compliance checks, but to thrive in the digital economy.
Use Case: How Top Fintechs Use Identity Verification

How Leading Fintechs Are Winning with Smart Identity Verification
PayPal
PayPal’s verification system goes beyond basic KYC checks by continuously analyzing:
- Transaction velocity patterns
- Behavioral biometrics
Wise
The global money transfer leader combines:
- AI-powered document verification (100+ ID types)
- Liveness detection to prevent photo spoofing
- Ongoing transaction monitoring
Revolut
Revolut’s verification framework demonstrates how to:
- Use NFC chip scanning for passport verification (reducing errors)
- Implement step-up authentication for high-risk transactions
- Maintain <90 second approval for 85% of applications
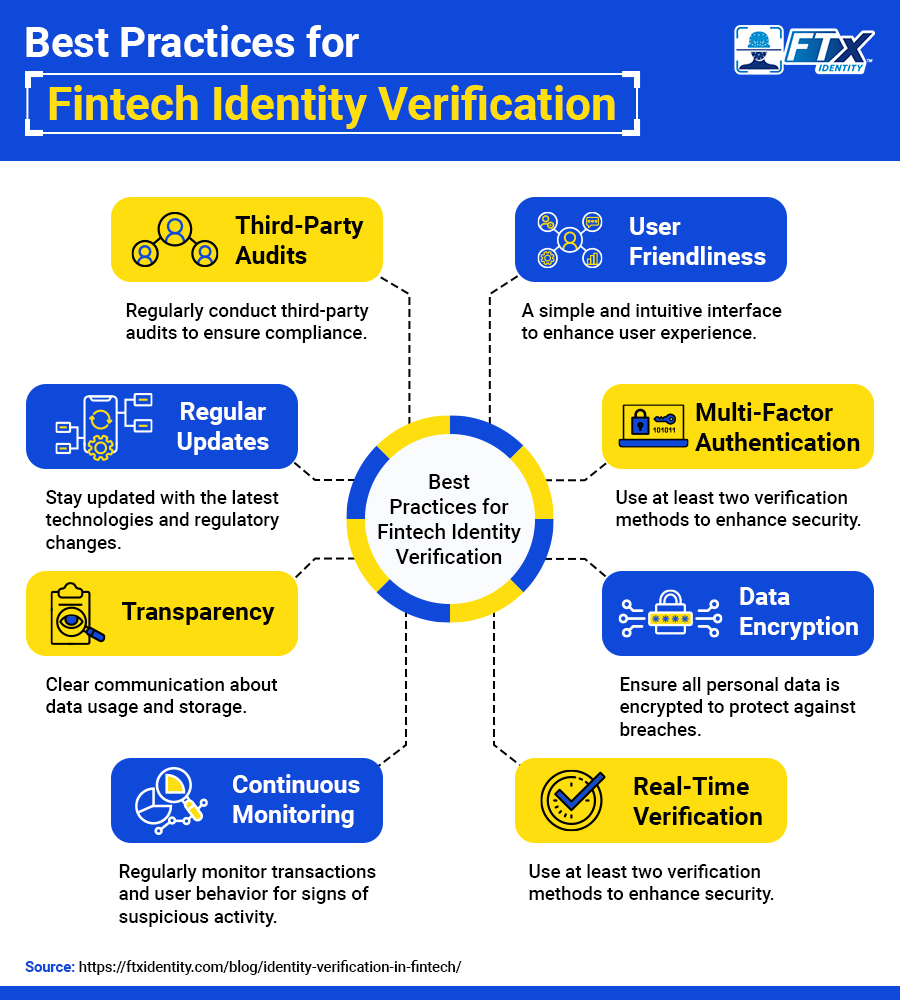
Best Practices for Implementing Fintech Identity Verification
Creating an effective identity verification framework requires balancing security, compliance, and user experience. These tactical best practices help fintechs optimize their verification processes:
1. Design Adaptive Verification Flows
Implement risk-based authentication that adjusts requirements based on:
- Transaction value
- User behavior patterns
- Geographic risk factors
2. Optimize Through Continuous Testing
Run A/B tests on onboarding flows to identify:
- Friction points causing drop-offs
- Optimal placement of verification steps
- Most effective authentication methods
3. Prioritize Mobile-First Accessibility
Ensure full functionality across:
- All mobile devices (including older models)
- Multiple language support
- Low-bandwidth environments
4. Layer Authentication Methods
Combine at least two verification factors:
- Document verification (passport, ID card)
- Biometric authentication (face match, liveness check)
5. Implement Smart Escalation Paths
Create clear protocols for flagged cases:
- Automated review for low-risk discrepancies
- Human review for potential fraud cases
- Fast-track approval for trusted repeat users
6. Maintain Ironclad Data Protection
- Encrypt all personal data in transit and at rest
- Implement zero-knowledge proof architecture where possible
- Conduct quarterly penetration testing
7. Stay Ahead of Compliance Changes
Assign dedicated compliance ops to monitor:
- Regional regulation updates
- Sanctions list changes
- New ID document formats
8. Build in Continuous Monitoring
Track post-onboarding activities:
- Transaction patterns
- Device changes
- Behavioral anomalies
Choosing the Right Identity Verification Partner for Your Fintech
Balancing Compliance and User Experience
The vendor selection process requires careful evaluation of whether a provider prioritizes:
- Compliance-first approach: Ideal for highly regulated sectors (crypto, cross-border payments) with rigorous document checks and audit trails
- UX-first approach: Better for consumer-facing apps needing frictionless onboarding, but may require additional compliance customization
Integration Capabilities That Drive Efficiency
Evaluate technical maturity through:
- API documentation quality and developer resources
- Pre-built connectors for major fintech stacks (Plaid, Stripe, etc.)
- Implementation timelines – top vendors enable go-live in <2 weeks
- Webhook support for real-time verification events
Customization and Scalability Needs
Your ideal partner should offer:
- Rule engine customization to adapt to unique risk models
- Geographic-specific workflows (Aadhaar verification in India, BankID in Scandinavia)
- Volume-based pricing that scales with your growth
- Modular architecture to add features like liveness detection later
Support Structures That Matter
Prioritize vendors offering:
1. 24/7 technical support with <1 hour response for critical issues
2. Dedicated compliance teams to navigate regulatory changes
3. Service-level agreement (SLA)-backed performance guarantees, including:
- Maximum false positive/negative rates
- Verification completion times
- System uptime commitments
Data Handling and Privacy Compliance
Essential safeguards to verify:
- Jurisdiction-specific data hosting (EU-only servers for GDPR)
- Certifications: SOC 2 Type II, ISO 27001, PCI DSS
- Data retention policies aligned with CCPA/GDPR requirements
- Encryption standards (AES-256 at minimum)
The Future of Identity Verification in Fintech
1. Reusable Digital Identities (eIDAS 2.0 & beyond)
The era of repetitive KYC checks is ending. The EU’s eIDAS 2.0 Digital Identity Wallets (2024 rollout) will allow users to store verified credentials once and reuse them across services. Expect:
– Cross-border interoperability (EU citizens using digital IDs for fintech onboarding globally)
– Self-sovereign identity (SSI) adoption, reducing fintech’s liability for storing personal data
2. Behavioral Biometrics: The Invisible Security Layer
Static verification will evolve into continuous authentication using:
– Typing cadence, swipe patterns, and mouse movements to detect account takeovers
– AI-powered anomaly detection flagging suspicious behavior in real-time
– Passive authentication (no extra steps for users) improving UX while cutting fraud

3. Privacy-First Verification Gains Momentum
Regulators and users demand less data exposure. Future solutions will leverage:
- Zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) – proving identity without revealing raw data
- Decentralized identifiers (DIDs) – users control who accesses their credentials
- On-device processing – biometrics verified locally, not stored centrally
4. AI-Driven Continuous Authentication
The shift from “verify once” to “always verify” means:
- Real-time risk scoring adjusts authentication strictness per transaction
- Generative AI detectors combat deepfake fraud at scale
- Predictive analytics flag high-risk users before fraud occurs
Fintechs that adopt these trends early will lead in both security and customer experience. The future of verification isn’t just about proving identity – it’s about doing so seamlessly, continuously, and privately.
Wrapping Up
Identity verification is no longer just a compliance hurdle – it’s a competitive advantage that balances robust security with seamless user experiences.
Fintechs that get this right:
- Prevent fraud without sacrificing conversion rates
- Scale globally while staying compliant
- Build trust that retains customers and attracts partners
Is Your Current Solution Future-Ready?
Take 5 minutes to assess your KYC stack:
- Does it adapt to new fraud tactics like deepfakes?
- Can it verify users in seconds, not days?
- Will it meet 2025’s regulations without costly reworks?
Don’t rely on outdated authentication methods.
Discover FTx Identity to:
- Stop fraud with advanced facial recognition and liveness detection
- Accelerate user onboarding by 90%
- Ensure compliance while scaling with confidence
